Java數組
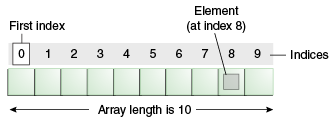
通常,數組是具有連續內存位置的類似類型的元素的集合。Java數組是一個包含類似數據類型的元素的對象。 它是一個數據結構,我們存儲類似的元素。 只能在java數組中存儲固定的元素集合。
java中的數組是基於索引的,數組的第一個元素存儲的索引爲:0。
Java Array的優點
代碼優化: 它使代碼優化,可以輕鬆地檢索或排序數據。
隨機訪問: 可以獲取任何位於任何索引位置的數據。
Java Array的缺點
大小限制: 只能在數組中存儲固定大小的元素。 它在運行時不會增長其大小。 爲了解決這個問題,在java中使用了集合框架。
java中的數組類型
有兩種類型的數組。
- 一維數組
- 多維數組
java中的單維數組
在java中聲明一個數組的語法。
dataType[] arr; (or)
dataType []arr; (or)
dataType arr[];在java中實例化數組
arrayRefVar=new datatype[size];一維java數組的示例
讓我們來看看java數組的簡單例子,下面聲明,實例化,初始化和遍歷數組。
class Testarray {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = new int[5];// declaration and instantiation
a[0] = 10;// initialization
a[1] = 20;
a[2] = 70;
a[3] = 40;
a[4] = 50;
// printing array
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)// length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}執行上面代碼的得到下面的結果 -
10
20
70
40
50Java數組的聲明,實例化和初始化
可以通過以下方式聲明,實例化和初始化java數組:
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization讓我們來看看打印數組的簡單例子。
class Testarray1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = { 33, 3, 4, 5 };// declaration, instantiation and
// initialization
// printing array
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)// length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下結果 -
33
3
4
5在Java中將數組傳遞給方法
我們可以將java數組傳遞給方法,以便可以在數組上重複使用相同的邏輯。
讓我們來看看獲取使用方法的數組的最小數的一個簡單的例子。
class Testarray2 {
static void min(int arr[]) {
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++)
if (min > arr[i])
min = arr[i];
System.out.println(min);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = { 33, 3, 4, 5 };
min(a);// passing array to method
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下結果 -
3**
java中的多維數組**
在這種情況下,數據存儲在基於行和列的索引(也稱爲矩陣形式)中。在Java中聲明多維數組的語法。
dataType[][] arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or)
dataType []arrayRefVar[];在java中實例化多維數組的示例
int[][] arr=new int[3][3];//3 row and 3 column在java中初始化多維數組的示例
arr[0][0]=1;
arr[0][1]=2;
arr[0][2]=3;
arr[1][0]=4;
arr[1][1]=5;
arr[1][2]=6;
arr[2][0]=7;
arr[2][1]=8;
arr[2][2]=9;多維java數組示例
讓我們來看看一個簡單的例子來聲明,實例化,初始化並打印二維數組。
class Testarray3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declaring and initializing 2D array
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 2, 4, 5 }, { 4, 4, 5 } };
// printing 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下結果 -
1 2 3
2 4 5
4 4 5java數組的類名是什麼?
在java中,數組是一個對象。 對於數組對象,創建一個代理類,其名稱可以通過對象上的getClass()。getName()方法獲取。
class Testarray4 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = { 4, 4, 5 };
Class c = arr.getClass();
String name = c.getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下代碼 -
I複製java數組
可以通過System類的arraycopy方法將數組複製到另一個數組。
arraycopy方法的語法
public static void arraycopy(
Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length
)arraycopy方法的示例
class TestArrayCopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] copyFrom = { 'd', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e', 'i', 'n', 'a', 't', 'e', 'd' };
char[] copyTo = new char[7];
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
System.out.println(new String(copyTo));
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下代碼 -
caffein在java中添加2個矩陣
讓我們來看看一個簡單的例子,添加兩個矩陣。
class Testarray5 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// creating two matrices
int a[][] = { { 1, 3, 4 }, { 3, 4, 5 } };
int b[][] = { { 1, 3, 4 }, { 3, 4, 5 } };
// creating another matrix to store the sum of two matrices
int c[][] = new int[2][3];
// adding and printing addition of 2 matrices
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
c[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j];
System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();// new line
}
}
}執行上面代碼,得到以下代碼 -
2 6 8
6 8 10