C語言指針
C語言中的指針是變量,也稱爲定位符或指示符,指向值的地址。
注意:指針是C語言的靈魂,如果指針不能熟練使用,那意味着你的C語言學得不咋地。
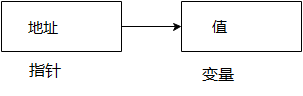
指針的優點
- 指針減少代碼並提高性能,用於檢索字符串,樹等,並與數組,結構和函數一起使用。
- 可以使用指針從函數返回多個值。
- 它使您能夠訪問計算機內存中的任何位置。
指針的使用
C語言中有很多指針的使用。
動態內存分配
在C語言中,可以指針使用malloc()和calloc()函數動態分配內存。數組,函數和結構
C語言中的指針被廣泛應用於數組,函數和結構中。它減少代碼並提高性能。
指針中使用的符號
符號
名稱
說明
&
地址運算符
確定變量的地址。
*
間接運算符
訪問地址上的值
地址運算符
地址運算符'&'返回變量的地址。 但是,我們需要使用%u來顯示變量的地址。創建一個源代碼文件:address-of-operator.c,其代碼實現如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int number = 50;
printf("value of number is %d, address of number is %u", number, &number);
}執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
value of number is 50, address of number is 15727016指針示例
下面給出了使用打印地址和值的指針的例子。如下圖所示 -
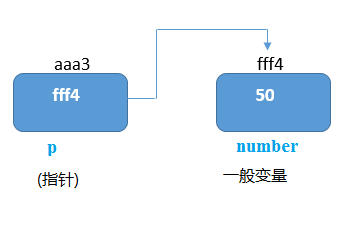
如上圖所示,指針變量存儲數字變量的地址,即fff4。數字變量的值爲50,但是指針變量p的地址是aaa3。
通過*(間接運算符)符號,可以打印指針變量p的值。
我們來看一下如上圖所示的指針示例。
創建一個源代碼文件:pointer-example.c,其代碼實現如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int number = 50;
int *p;
p = &number;//stores the address of number variable
printf("Address of number variable is %x \n", &number);
printf("Address of p variable is %x \n", p);
printf("Value of p variable is %d \n", *p);
}執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Address of number variable is b3fa4c
Address of p variable is b3fa4c
Value of p variable is 50NULL指針
未分配任何值的指針稱爲NULL指針。 如果在聲明時沒有在指針中指定任何地址,則可以指定NULL值,這將是一個更好的方法。
int *p=NULL;在大多數庫中,指針的值爲0(零)。
指針的應用示例:
指針程序來交換2個數字而不使用第3個變量
創建一個源代碼文件:swap2numbers.c,其代碼實現如下 -
#include<stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 10, b = 20, *p1 = &a, *p2 = &b;
printf("Before swap: *p1=%d *p2=%d\n", *p1, *p2);
*p1 = *p1 + *p2;
*p2 = *p1 - *p2;
*p1 = *p1 - *p2;
printf("\nAfter swap: *p1=%d *p2=%d\n", *p1, *p2);
}執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Before swap: *p1=10 *p2=20
After swap: *p1=20 *p2=10