Java static關鍵字
java中的static關鍵字主要用於內存管理。我們可以應用java static關鍵字在變量,方法,塊和嵌套類中。 static關鍵字屬於類,而不是類的實例。
靜態(static)可以是:
- 變量(也稱爲類變量)
- 方法(也稱爲類方法)
- 代碼塊
- 嵌套類
1. Java靜態變量
如果將一個變量聲明爲static,它就是所謂的靜態變量了。
- 靜態變量可以用於引用所有對象的公共屬性(對於每個對象不是唯一的)。如:員工公司名稱,學生所在的大學名稱。
靜態變量的優點:
- 它能使程序存儲器高效(即它節省內存)。
理解不使用靜態變量的問題
class Student{
int rollno;
String name;
String college="ITS";
}假設在一所學校有500名學生,現在所有實例數據成員將在每次創建對象時獲取內存。所有學生都有其唯一的註冊ID:rollno和 name ,因此實例數據成員沒有什麼問題。college 指的是所有對象的共同屬性。如果使它靜態化(使用static關鍵字修飼),這個字段將只獲得內存一次。
Java靜態屬性被共享給所有對象。
靜態變量的示例
//Program of static variable
class Student8 {
int rollno;
String name;
static String college = "ITS";
Student8(int r, String n) {
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + college);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student8 s1 = new Student8(111, "Karan");
Student8 s2 = new Student8(222, "Aryan");
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}上面代碼執行結果如下 -
111 Karan ITS
222 Aryan ITS創建對象示例圖如下所示 -
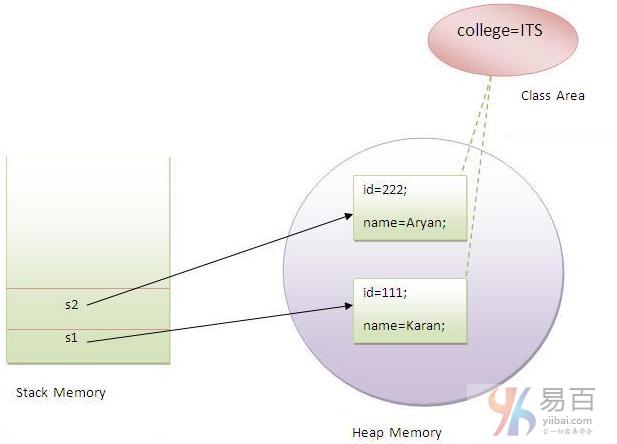
不使用靜態變量的計數器程序
在這個例子中,我們創建了一個名爲count的實例變量用來統計創建對象的數目,它在構造函數中執行遞增。 由於實例變量在創建對象時要獲取內存,每個對象都將具有實例變量的副本,如果它被遞增了,它也不會反映到其他對象中。所以每個對象在count變量中的值還是1。
class Counter {
int count = 0;// will get memory when instance is created
Counter() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Counter c1 = new Counter();
Counter c2 = new Counter();
Counter c3 = new Counter();
}
}上面代碼執行結果如下 -
1
1
1計數器靜態變量的程序
如上所述,靜態變量將只獲取一次內存,如果任何對象更改靜態變量的值,它將保留其值,所有實例均可訪問同一變量值。
class Counter2 {
static int count = 0;// will get memory only once and retain its value
Counter2() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Counter2 c1 = new Counter2();
Counter2 c2 = new Counter2();
Counter2 c3 = new Counter2();
}
}上面代碼執行結果如下 -
1
2
32. Java靜態方法
如果在任何方法上應用static關鍵字,此方法稱爲靜態方法。
- 靜態方法屬於類,而不屬於類的對象。
- 可以直接調用靜態方法,而無需創建類的實例。
- 靜態方法可以訪問靜態數據成員,並可以更改靜態數據成員的值。
靜態方法的示例
//Program of changing the common property of all objects(static field).
class Student9 {
int rollno;
String name;
static String college = "ITS";
static void change() {
college = "BBDIT";
}
Student9(int r, String n) {
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + college);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student9.change();
Student9 s1 = new Student9(111, "Karan");
Student9 s2 = new Student9(222, "Aryan");
Student9 s3 = new Student9(333, "Sonoo");
s1.display();
s2.display();
s3.display();
}
}上面代碼執行輸出以下結果 -
111 Karan BBDIT
222 Aryan BBDIT
333 Sonoo BBDIT執行正常計算的靜態方法的另一個示例:
//Program to get cube of a given number by static method
class Calculate {
static int cube(int x) {
return x * x * x;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result = Calculate.cube(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
}上面代碼執行輸出以下結果 -
125靜態方法的限制
靜態方法有兩個主要限制。它們分別是:
- 靜態方法不能直接使用非靜態數據成員或調用非靜態方法。
-
this和super兩個關鍵字不能在靜態上下文中使用。
class A {
int a = 40;// non static
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}上面代碼執行輸出以下結果 -
[編譯錯誤!]Compile Time Error爲什麼java main方法是靜態的?
這是因爲對象不需要調用靜態方法,如果它是非靜態方法,jvm首先要創建對象,然後調用main()方法,這將導致額外的內存分配的問題。
3. Java靜態塊
Java中的靜態塊主要有兩個作用:
- 用於初始化靜態數據成員。
- 它在類加載時在main方法之前執行。
靜態塊的示例
class A2 {
static {
System.out.println("static block is invoked");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello main");
}
}上面代碼執行輸出以下結果 -
static block is invoked
Hello main可以執行程序沒有main()方法嗎?
答:是的,一種方式是靜態塊,但在以前舊的JDK版本中,不是在JDK 1.7。
class A3 {
static {
System.out.println("static block is invoked");
System.exit(0);
}
}上面代碼執行輸出以下結果 -
static block is invoked在JDK7及以上版本中,輸出將爲:
錯誤: 在類 Main 中找不到 main 方法, 請將 main 方法定義爲:
public static void main(String[] args)