Scipy Linalg
SciPy是使用優化的ATLAS LAPACK和BLAS庫構建的。 它具有非常快的線性代數能力。 所有這些線性代數例程都需要一個可以轉換爲二維數組的對象。 這些例程的輸出也是一個二維數組。
SciPy.linalg與NumPy.linalg
scipy.linalg包含numpy.linalg中的所有函數。 另外,scipy.linalg還有一些不在numpy.linalg中的高級函數。 在numpy.linalg上使用scipy.linalg的另一個優點是它總是用BLAS/LAPACK支持編譯,而對於NumPy,這是可選的。 因此,根據NumPy的安裝方式,SciPy版本可能會更快。
線性方程組
scipy.linalg.solve特徵爲未知的x,y值求解線性方程a * x + b * y = Z。
作爲一個例子,假設需要解下面的聯立方程。
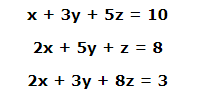
要求解x,y,z值的上述方程式,可以使用矩陣求逆來求解向量,如下所示。
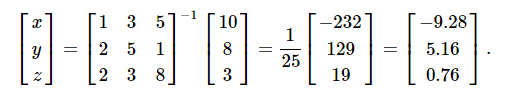
但是,最好使用linalg.solve命令,該命令可以更快,更穩定。
求解函數採用兩個輸入'a'和'b',其中'a'表示係數,'b'表示相應的右側值並返回解矩陣。
現在來看看下面的例子。
#importing the scipy and numpy packages
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
#Declaring the numpy arrays
a = np.array([[3, 2, 0], [1, -1, 0], [0, 5, 1]])
b = np.array([2, 4, -1])
#Passing the values to the solve function
x = linalg.solve(a, b)
#printing the result array
print (x)執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
[ 2. -2. 9.]查找一個行列式
方陣A的行列式通常表示爲| A |並且是線性代數中經常使用的量。 在SciPy中,這是使用det()函數計算的。 它將矩陣作爲輸入並返回一個標量值。
下面來看看一個例子。
#importing the scipy and numpy packages
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
#Declaring the numpy array
A = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
#Passing the values to the det function
x = linalg.det(A)
#printing the result
print (x)執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
-2.0特徵值和特徵向量
特徵值 - 特徵向量問題是最常用的線性代數運算之一。 我們可以通過考慮以下關係式來找到方陣(A)的特徵值(λ)和相應的特徵向量(v)
Av = λvscipy.linalg.eig從普通或廣義特徵值問題計算特徵值。 該函數返回特徵值和特徵向量。
讓我們來看看下面的例子。
#importing the scipy and numpy packages
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
#Declaring the numpy array
A = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
#Passing the values to the eig function
l, v = linalg.eig(A)
#printing the result for eigen values
print (l)
#printing the result for eigen vectors
print (v)執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
[-0.37228132+0.j 5.37228132+0.j]
[[-0.82456484 -0.41597356]
[ 0.56576746 -0.90937671]]奇異值分解
奇異值分解(SVD)可以被認爲是特徵值問題擴展到非矩陣的矩陣。
scipy.linalg.svd將矩陣'a'分解爲兩個酉矩陣'U'和'Vh',以及一個奇異值(實數,非負)的一維數組's',使得a == U * S * Vh,其中'S'是具有主對角線's'的適當形狀的零點矩陣。
讓我們來看看下面的例子。參考以下代碼 -
#importing the scipy and numpy packages
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
#Declaring the numpy array
a = np.random.randn(3, 2) + 1.j*np.random.randn(3, 2)
#Passing the values to the eig function
U, s, Vh = linalg.svd(a)
# printing the result
print (U, Vh, s)執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
[[-0.60142679+0.28212127j 0.35719830-0.03260559j 0.61548126-0.22632383j]
[-0.00477296+0.44250532j 0.64058557+0.15734719j -0.40414313+0.45357092j]
[ 0.46360086+0.38462177j -0.18611686+0.6337182j 0.44311251+0.06747886j]] [[ 0.98724353+0.j -0.01113675+0.15882756j]
[-0.15921753+0.j -0.06905445+0.9848255j ]] [ 2.04228408 1.33798044]