C#運算符
運算符只是一個用於執行操作的符號。可以有許多類型的操作,如算術,邏輯,按位等運算操作。
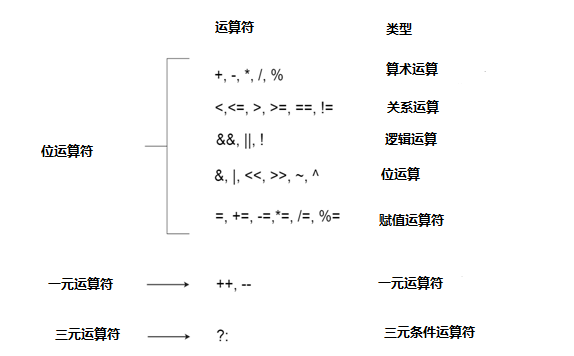
有以下類型的運算符可以在 C# 語言中執行不同類型的操作運算。
- 算術運算符
- 關係運營商
- 邏輯運算符
- 按位運算符
- 賦值運算符
- 其它運算符
1. 算術運算符
下面示例代碼演示 C# 如何使用算術運算符。假設變量A的值爲:10,變量B的值爲:20,參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
int c;
c = a + b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a - b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a * b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a / b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a % b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a++;
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a--;
Console.WriteLine("Line 7 - Value of c is {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Line 1 - Value of c is 31
Line 2 - Value of c is 11
Line 3 - Value of c is 210
Line 4 - Value of c is 2
Line 5 - Value of c is 1
Line 6 - Value of c is 22
Line 7 - Value of c is 202. 關係運算符
下面示例代碼演示 C# 如何使用關係運算符。 假設變量A的值爲:10,變量B的值爲:20,參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
if (a == b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - a is equal to b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - a is not equal to b");
}
if (a < b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - a is less than b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - a is not less than b");
}
if (a > b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - a is greater than b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - a is not greater than b");
}
/* Lets change value of a and b */
a = 5;
b = 20;
if (a <= b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - a is either less than or equal to b");
}
if (b >= a)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 5-b is either greater than or equal to b");
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Line 1 - a is not equal to b
Line 2 - a is not less than b
Line 3 - a is greater than b
Line 4 - a is either less than or equal to b
Line 5 - b is either greater than or equal to b3. 邏輯運算符
下面示例代碼演示 C# 如何使用邏輯運算符。 假設變量A是一個布爾值:true,變量B是一個布爾值:false,參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a = true;
bool b = true;
if (a && b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - Condition is true");
}
if (a || b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - Condition is true");
}
/* lets change the value of a and b */
a = false;
b = true;
if (a && b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - Condition is true");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - Condition is not true");
}
if (!(a && b))
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - Condition is true");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Line 1 - Condition is true
Line 2 - Condition is true
Line 3 - Condition is not true
Line 4 - Condition is true4. 位運算符
下面將通過示例來演示 C# 如何使用按位運算符。 假設變量A的值爲:60,變量B的值爲:13,參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */
int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */
int c = 0;
c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - Value of c is {0}", c );
c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - Value of c is {0}", c);
c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - Value of c is {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Line 1 - Value of c is 12
Line 2 - Value of c is 61
Line 3 - Value of c is 49
Line 4 - Value of c is -61
Line 5 - Value of c is 240
Line 6 - Value of c is 155. 賦值運算符
有關 C# 如何使用賦值運算符,請參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int c;
c = a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - = Value of c = {0}", c);
c += a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - += Value of c = {0}", c);
c -= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - -= Value of c = {0}", c);
c *= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - *= Value of c = {0}", c);
c /= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - /= Value of c = {0}", c);
c = 200;
c %= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - %= Value of c = {0}", c);
c <<= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 7 - <<= Value of c = {0}", c);
c >>= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 8 - >>= Value of c = {0}", c);
c &= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 9 - &= Value of c = {0}", c);
c ^= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 10 - ^= Value of c = {0}", c);
c |= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 11 - |= Value of c = {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Line 1 - = Value of c = 21
Line 2 - += Value of c = 42
Line 3 - -= Value of c = 21
Line 4 - *= Value of c = 441
Line 5 - /= Value of c = 21
Line 6 - %= Value of c = 11
Line 7 - <<= Value of c = 44
Line 8 - >>= Value of c = 11
Line 9 - &= Value of c = 2
Line 10 - ^= Value of c = 0
Line 11 - |= Value of c = 26. 其他運算符
還有其他幾個重要的操作符,包括sizeof,typeof和?:等也被 C# 支持。請參考以下示例代碼:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* example of sizeof operator */
Console.WriteLine("The size of int is {0}", sizeof(int));
Console.WriteLine("The size of short is {0}", sizeof(short));
Console.WriteLine("The size of double is {0}", sizeof(double));
/* example of ternary operator */
int a, b;
a = 10;
b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30;
Console.WriteLine("Value of b is {0}", b);
b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30;
Console.WriteLine("Value of b is {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
The size of int is 4
The size of short is 2
The size of double is 8
Value of b is 30
Value of b is 207. C# 中的運算符優先級
運算符的優先級指定哪個運算符將被首先評估計算。關聯性指定要評估的操作符方向,可以是左到右,或從右到左。
下面給出一個優先級的例子代碼:
int data= 10+ 5*5 ;data變量最後的計算值爲:35,因爲*(乘法運算符)在+(加法運算符)之前求值。
C語言運算符的優先級和關聯性如下:
分類
運算符
關聯性
後綴
() [] -> . ++ - -
左到右
一元
+ - ! ~ ++ - - (type)* & sizeof
右到左
乘法
* / %
左到右
加法
+ -
左到右
位移
<< >>
左到右
關係
< <= > >=
左到右
等於
== !=
左到右
按位與
&
左到右
位異或
^
左到右
按位或
/
左到右
邏輯與
&&
左到右
邏輯或
//
左到右
條件
?:
右到左
賦值
= += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= /=
右到左
逗號
,
左到右
示例
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 20;
int b = 10;
int c = 15;
int d = 5;
int e;
e = (a + b) * c / d; // ( 30 * 15 ) / 5
Console.WriteLine("Value of (a + b) * c / d is : {0}", e);
e = ((a + b) * c) / d; // (30 * 15 ) / 5
Console.WriteLine("Value of ((a + b) * c) / d is : {0}", e);
e = (a + b) * (c / d); // (30) * (15/5)
Console.WriteLine("Value of (a + b) * (c / d) is : {0}", e);
e = a + (b * c) / d; // 20 + (150/5)
Console.WriteLine("Value of a + (b * c) / d is : {0}", e);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}當編譯和執行上述代碼時,會產生以下結果:
Value of (a + b) * c / d is : 90
Value of ((a + b) * c) / d is : 90
Value of (a + b) * (c / d) is : 90
Value of a + (b * c) / d is : 50