XML DOM導航
到目前爲止,我們已經學習了DOM結構,如何加載和解析XML DOM對象以及遍歷DOM對象。 在這節中看到如何在DOM對象中的節點之間導航。 XML DOM包含節點的各種屬性,可用於瀏覽節點,例如 -
-
parentNode -
childNodes -
firstChild -
lastChild -
nextSibling -
previousSibling
以下是節點樹的示意圖,顯示節點之間的關係。
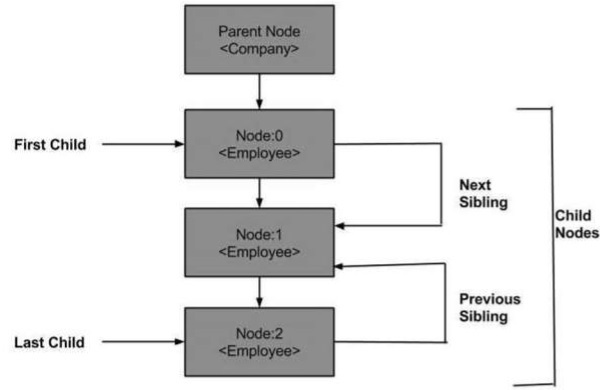
1. DOM父節點
此屬性將父節點指定爲節點對象。
示例
以下示例(navigate_example.html)將XML文檔(node.xml)解析爲XML DOM對象。
文件:node.xml -
<Company>
<Employee category = "Technical" id = "firstelement">
<FirstName>Susen</FirstName>
<LastName>Su</LastName>
<ContactNo>1584567890</ContactNo>
<Email>[email protected]</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Non-Technical">
<FirstName>Max</FirstName>
<LastName>Su</LastName>
<ContactNo>1334667898</ContactNo>
<Email>[email protected]</Email>
</Employee>
<Employee category = "Management">
<FirstName>Min</FirstName>
<LastName>Su</LastName>
<ContactNo>1364562350</ContactNo>
<Email>[email protected]</Email>
</Employee>
</Company>然後DOM對象通過子節點導航到父節點,文件:navigate_example.html -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
var y = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0];
document.write(y.parentNode.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>如上例所示,子節點Employee導航到它的父節點。
執行
將此文件保存到web服務器命名爲:navigate_example.html(此文件和node.xml應位於服務器中的同一目錄中)。 在輸出中得到Employee的父節點,即:Company。
2. 最後一個子節點
此屬性的類型爲Node,表示NodeList中存在的最後一個子名稱。
示例
以下示例(last_node.html)將XML文檔(node.xml)解析爲XML DOM對象,然後導航到XML DOM對象中存在的最後一個子節點。
文件:last_node.html -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_lastChild(p) {
a = p.lastChild;
while (a.nodeType != 1){
a = a.previousSibling;
}
return a;
}
var lastchild = get_lastChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Employee")[0]);
document.write(lastchild.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>執行
將此文件last_node.html 保存到web服務器目錄(此文件和node.xml應位於服務器的同一路徑上)。 在輸出結果中可能看到Employee的最後一個子節點,即Email。
3. 下一個兄弟節點
此屬性是Node類型,表示下一個子節點,即NodeList中指定的子元素的下一個兄弟節點。
示例
以下示例(next-sibling.html )將XML文檔(node.xml)解析爲XML DOM對象,該對象立即導航到xml文檔中存在的下一個節點。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_nextSibling(p) {
a = p.nextSibling;
while (a.nodeType != 1) {
a = a.nextSibling;
}
return a;
}
var nextsibling = get_nextSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("FirstName")[0]);
document.write(nextsibling.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>執行
將此文件保存爲:nextSibling_example.html,在Web服務器路徑上(此文件和node.xml應位於服務器中的同一路徑上)。 在輸出中得到FirstName的下一個兄弟節點,即LastName。
4. 之前的兄弟節點
此屬性的類型爲Node,表示前一個子節點,即NodeList中指定的子元素的前一個兄弟節點。
示例
以下示例(previoussibling.html)將XML文檔(node.xml)解析爲XML DOM對象,然後導航xml文檔中存在的最後一個子節點的之前節點。
文件:previoussibling.html -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest)
{
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/node.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc = xmlhttp.responseXML;
function get_previousSibling(p) {
a = p.previousSibling;
while (a.nodeType != 1) {
a = a.previousSibling;
}
return a;
}
prevsibling = get_previousSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("Email")[0]);
document.write(prevsibling.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>執行
將此文件保存爲:previoussibling.html,在WEB服務器路徑上的(此文件和node.xml應位於服務器的同一路徑上)。 在輸出中得到了Email的前一個兄弟節點,即ContactNo。