Pandas數據幀(DataFrame)
數據幀(DataFrame)是二維數據結構,即數據以行和列的表格方式排列。
數據幀(DataFrame)的功能特點:
- 潛在的列是不同的類型
- 大小可變
- 標記軸(行和列)
- 可以對行和列執行算術運算
結構體
假設要創建一個包含學生數據的數據幀。參考以下圖示 -
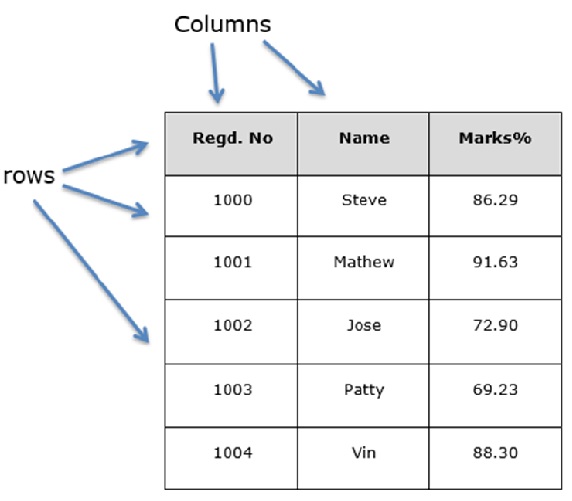
可以將上圖表視爲SQL表或電子表格數據表示。
pandas.DataFrame
pandas中的DataFrame可以使用以下構造函數創建 -
pandas.DataFrame( data, index, columns, dtype, copy)構造函數的參數如下 -
編號
參數
描述
1
data
數據採取各種形式,如:ndarray,series,map,lists,dict,constant和另一個DataFrame。
2
index
對於行標籤,要用於結果幀的索引是可選缺省值np.arrange(n),如果沒有傳遞索引值。
3
columns
對於列標籤,可選的默認語法是 - np.arange(n)。 這隻有在沒有索引傳遞的情況下才是這樣。
4
dtype
每列的數據類型。
5
copy
如果默認值爲False,則此命令(或任何它)用於複製數據。
創建DataFrame
Pandas數據幀(DataFrame)可以使用各種輸入創建,如 -
- 列表
- 字典
- 系列
- Numpy ndarrays
- 另一個數據幀(DataFrame)
在本章的後續章節中,我們將看到如何使用這些輸入創建數據幀(DataFrame)。
創建一個空的DataFrame
創建基本數據幀是空數據幀。
示例
#import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame()
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []從列表創建DataFrame
可以使用單個列表或列表列表創建數據幀(DataFrame)。
實例-1
import pandas as pd
data = [1,2,3,4,5]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
0
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5實例-2
import pandas as pd
data = [['Alex',10],['Bob',12],['Clarke',13]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'])
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Name Age
0 Alex 10
1 Bob 12
2 Clarke 13實例-3
import pandas as pd
data = [['Alex',10],['Bob',12],['Clarke',13]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'],dtype=float)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Name Age
0 Alex 10.0
1 Bob 12.0
2 Clarke 13.0注意 - 可以觀察到,
dtype參數將Age列的類型更改爲浮點。
從ndarrays/Lists的字典來創建DataFrame
所有的ndarrays必須具有相同的長度。如果傳遞了索引(index),則索引的長度應等於數組的長度。
如果沒有傳遞索引,則默認情況下,索引將爲range(n),其中n爲數組長度。
實例-1
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Age Name
0 28 Tom
1 34 Jack
2 29 Steve
3 42 Ricky注 - 觀察值
0,1,2,3。它們是分配給每個使用函數range(n)的默認索引。
示例-2
使用數組創建一個索引的數據幀(DataFrame)。
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['rank1','rank2','rank3','rank4'])
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Age Name
rank1 28 Tom
rank2 34 Jack
rank3 29 Steve
rank4 42 Ricky注意 -
index參數爲每行分配一個索引。
從列表創建數據幀DataFrame
字典列表可作爲輸入數據傳遞以用來創建數據幀(DataFrame),字典鍵默認爲列名。
實例-1
以下示例顯示如何通過傳遞字典列表來創建數據幀(DataFrame)。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
a b c
0 1 2 NaN
1 5 10 20.0注意 - 觀察到,NaN(不是數字)被附加在缺失的區域。
示例-2
以下示例顯示如何通過傳遞字典列表和行索引來創建數據幀(DataFrame)。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'])
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
a b c
first 1 2 NaN
second 5 10 20.0實例-3
以下示例顯示如何使用字典,行索引和列索引列表創建數據幀(DataFrame)。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
#With two column indices, values same as dictionary keys
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'], columns=['a', 'b'])
#With two column indices with one index with other name
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'], columns=['a', 'b1'])
print df1
print df2執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
#df1 output
a b
first 1 2
second 5 10
#df2 output
a b1
first 1 NaN
second 5 NaN注意 - 觀察,
df2使用字典鍵以外的列索引創建DataFrame; 因此,附加了NaN到位置上。 而df1是使用列索引創建的,與字典鍵相同,所以也附加了NaN。
從系列的字典來創建DataFrame
字典的系列可以傳遞以形成一個DataFrame。 所得到的索引是通過的所有系列索引的並集。
示例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df
`執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
one two
a 1.0 1
b 2.0 2
c 3.0 3
d NaN 4注意 - 對於第一個系列,觀察到沒有傳遞標籤
'd',但在結果中,對於d標籤,附加了NaN。
現在通過實例來了解列選擇,添加和刪除。
列選擇
下面將通過從數據幀(DataFrame)中選擇一列。
示例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df ['one']執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
a 1.0
b 2.0
c 3.0
d NaN
Name: one, dtype: float64列添加
下面將通過向現有數據框添加一個新列來理解這一點。
示例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
# Adding a new column to an existing DataFrame object with column label by passing new series
print ("Adding a new column by passing as Series:")
df['three']=pd.Series([10,20,30],index=['a','b','c'])
print df
print ("Adding a new column using the existing columns in DataFrame:")
df['four']=df['one']+df['three']
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Adding a new column by passing as Series:
one two three
a 1.0 1 10.0
b 2.0 2 20.0
c 3.0 3 30.0
d NaN 4 NaN
Adding a new column using the existing columns in DataFrame:
one two three four
a 1.0 1 10.0 11.0
b 2.0 2 20.0 22.0
c 3.0 3 30.0 33.0
d NaN 4 NaN NaN列刪除
列可以刪除或彈出; 看看下面的例子來了解一下。
例子
# Using the previous DataFrame, we will delete a column
# using del function
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']),
'three' : pd.Series([10,20,30], index=['a','b','c'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print ("Our dataframe is:")
print df
# using del function
print ("Deleting the first column using DEL function:")
del df['one']
print df
# using pop function
print ("Deleting another column using POP function:")
df.pop('two')
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Our dataframe is:
one three two
a 1.0 10.0 1
b 2.0 20.0 2
c 3.0 30.0 3
d NaN NaN 4
Deleting the first column using DEL function:
three two
a 10.0 1
b 20.0 2
c 30.0 3
d NaN 4
Deleting another column using POP function:
three
a 10.0
b 20.0
c 30.0
d NaN行選擇,添加和刪除
現在將通過下面實例來了解行選擇,添加和刪除。我們從選擇的概念開始。
標籤選擇
可以通過將行標籤傳遞給loc()函數來選擇行。參考以下示例代碼 -
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df.loc['b']執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
one 2.0
two 2.0
Name: b, dtype: float64結果是一系列標籤作爲DataFrame的列名稱。 而且,系列的名稱是檢索的標籤。
按整數位置選擇
可以通過將整數位置傳遞給iloc()函數來選擇行。參考以下示例代碼 -
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df.iloc[2]執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
one 3.0
two 3.0
Name: c, dtype: float64行切片
可以使用:運算符選擇多行。參考以下示例代碼 -
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df[2:4]執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
one two
c 3.0 3
d NaN 4附加行
使用append()函數將新行添加到DataFrame。 此功能將附加行結束。
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2], [3, 4]], columns = ['a','b'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame([[5, 6], [7, 8]], columns = ['a','b'])
df = df.append(df2)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
a b
0 1 2
1 3 4
0 5 6
1 7 8刪除行
使用索引標籤從DataFrame中刪除或刪除行。 如果標籤重複,則會刪除多行。
如果有注意,在上述示例中,有標籤是重複的。這裏再多放一個標籤,看看有多少行被刪除。
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2], [3, 4]], columns = ['a','b'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame([[5, 6], [7, 8]], columns = ['a','b'])
df = df.append(df2)
# Drop rows with label 0
df = df.drop(0)
print df執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
a b
1 3 4
1 7 8在上面的例子中,一共有兩行被刪除,因爲這兩行包含相同的標籤0。
以下是糾正/補充內容:
這裏錯了不是arange而應該是arrange。 提交時間:2019-10-25