Secure Spring REST API使用基本認證
假設您想保護應用程序的REST API,要怎麼做? 有幾種流行的方式做到這一點,從基本身份驗證到一個完全成熟的OAuth2安全解決方案。 本教程文章中將介紹使用基本安全身份驗證,涉及兩個獨立的客戶實例來測試REST API:【Postman和基於Spring RestTemplate的Java應用程序】,現在使用它們來試着訪問REST API。我們將在接下來的文章展示 OAuth2 用戶相同的例子: 使用OAuth2 REST API
與往常一樣,完整的代碼可以在本文的末尾下載。
如果您正在使用基本身份驗證,可查看AngularJS應用基礎: AngularJS使用Spring Securyt的基礎認證 這篇文章中顯示瞭如何使用AngularJS客戶端。
什麼是基本身份驗證?
如基於Web的客戶端的登錄頁面或會話身份驗證的傳統方法與人類有良好的互動效果,但並不能完全適合很好地應用,[REST]客戶端它不止只一個Web應用程序進行通信時。考慮它是一個完全不同於服務器上的其他API,它隨時都會與服務器的API通信,無需任何人爲干預。
基本身份驗證它提供了一個方法來解決這個問題,雖然不是很安全。基本身份驗證,客戶端的每個請求發送Base64編碼憑據,使用HTTP[授權]頭。這意味着每個請求獨立於其他請求和服務器可能/不維護客戶端,這對可擴展性是非常好的。
在HTTPS個詞:對於任何形式的安全實現,從基本身份驗證到一個完全成熟的 OAuth2 實現,HTTPS都是具備的。如果沒有HTTPS,不管你的實現是什麼,安全性是容易受到損害。
下面示出的是準備標頭的樣本代碼。
String plainClientCredentials="myusername:mypassword";
String base64ClientCredentials = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(plainClientCredentials.getBytes()));
HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", "Basic " + base64ClientCredentials);因而可能會產生這樣的結果:
Authorization : Basic bXktdHJ1c3RlZC1jbGllbnQ6c2VjcmV0...
這個頭將和每個請求一起發送。由於證書[Base 64編碼,甚至不加密]要和每個請求一起發送,這樣安全就可能受到損害。爲了防止這一點,使用的一種方式是在基本認證時也使用HTTPS。
基本身份驗證和Spring Security
有兩個步驟,就可以啓用基本身份驗證在Spring Security配置中。
1. 配置httpBasic : 配置HTTP基本身份驗證。 [基於HTTP的XML]
2. 配置有BasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai認證入口點 : 如果驗證失敗[無效/缺少憑據],這個切入點將被觸發。 這是非常重要的,因爲我們不想重定向到身份驗證失敗的登錄頁面[Spring Security的默認行爲] ,因爲這裏我們沒有一個登錄頁面。
下面顯示的是基於HTTP和切入點建立完整的 Spring Security 配置。
package com.yiibai.springmvc.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private static String REALM="MY\_TEST\_REALM";
@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("bill").password("abc123").roles("ADMIN");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("tom").password("abc123").roles("USER");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/\*\*").hasRole("ADMIN")
.and().httpBasic().realmName(REALM).authenticationEntryYiibai(getBasicAuthEntryYiibai())
.and().sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);//We don't need sessions to be created.
}
@Bean
public CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai getBasicAuthEntryYiibai(){
return new CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai();
}
/\* To allow Pre-flight \[OPTIONS\] request from browser \*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/\*\*");
}}
而從實際的切入點,如果驗證失敗將觸發程序處理。您可以自定義它來響應發送自定義的內容。
package com.yiibai.springmvc.security;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai;
public class CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai extends BasicAuthenticationEntryYiibai {
@Override
public void commence(final HttpServletRequest request,
final HttpServletResponse response,
final AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
//Authentication failed, send error response.
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC\_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName() + "");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 : " + authException.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
setRealmName("MY\_TEST\_REALM");
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}}
這就是需要配置基本安全。現在,讓我們來看看動作中的一切,這裏用之前老的REST API:
REST API
簡單的Spring REST API,它的服務器用戶(客戶可以使用標準的HTML動詞,符合REST風格來執行CRUD操作。
package com.yiibai.springmvc.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import com.yiibai.springmvc.model.User;
import com.yiibai.springmvc.service.UserService;
@RestController
public class HelloWorldRestController {
@Autowired
UserService userService; //Service which will do all data retrieval/manipulation work
//-------------------Retrieve All Users--------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> listAllUsers() {
List<User> users = userService.findAllUsers();
if(users.isEmpty()){
return new ResponseEntity<List<User>>(HttpStatus.NO\_CONTENT);//You many decide to return HttpStatus.NOT\_FOUND
}
return new ResponseEntity<List<User>>(users, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//-------------------Retrieve Single User--------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION\_JSON\_VALUE,MediaType.APPLICATION\_XML\_VALUE})
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
System.out.println("Fetching User with id " + id);
User user = userService.findById(id);
if (user == null) {
System.out.println("User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT\_FOUND);
}
return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//-------------------Create a User--------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<Void> createUser(@RequestBody User user, UriComponentsBuilder ucBuilder) {
System.out.println("Creating User " + user.getName());
if (userService.isUserExist(user)) {
System.out.println("A User with name " + user.getName() + " already exist");
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
}
userService.saveUser(user);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(ucBuilder.path("/user/{id}").buildAndExpand(user.getId()).toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
//------------------- Update a User --------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("Updating User " + id);
User currentUser = userService.findById(id);
if (currentUser==null) {
System.out.println("User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT\_FOUND);
}
currentUser.setName(user.getName());
currentUser.setAge(user.getAge());
currentUser.setSalary(user.getSalary());
userService.updateUser(currentUser);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(currentUser, HttpStatus.OK);
}
//------------------- Delete a User --------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<User> deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
System.out.println("Fetching & Deleting User with id " + id);
User user = userService.findById(id);
if (user == null) {
System.out.println("Unable to delete. User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT\_FOUND);
}
userService.deleteUserById(id);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NO\_CONTENT);
}
//------------------- Delete All Users --------------------------------------------------------
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<User> deleteAllUsers() {
System.out.println("Deleting All Users");
userService.deleteAllUsers();
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NO\_CONTENT);
}}
運行應用程序
構建和部署應用程序到Web容器[例如Tomcat]。運行它,並使用兩種不同的客戶端進行測試。
使用客戶1: Postman
發送一個請求來獲取用戶列表。請求URL: http://localhost:8080/SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication/user/,將會得到一個401。
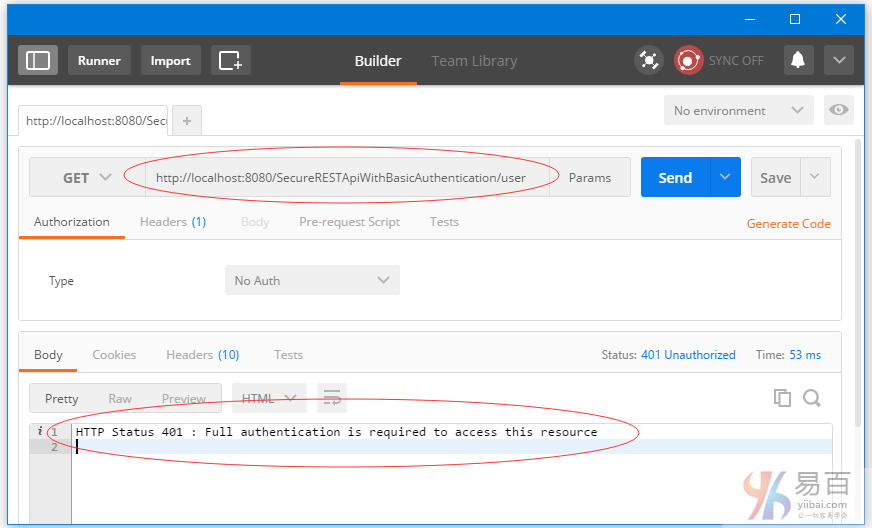
現在,從下拉列表中選擇類型(Type)爲 ‘Basic Auth’,填寫用戶名/密碼[bill/abc123],,點擊 ‘update request’。如下圖中所示 -
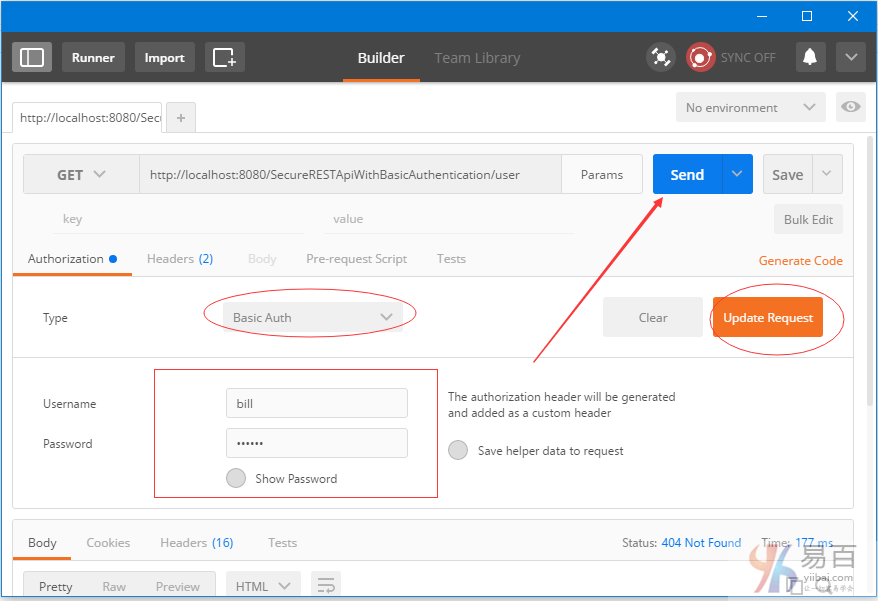
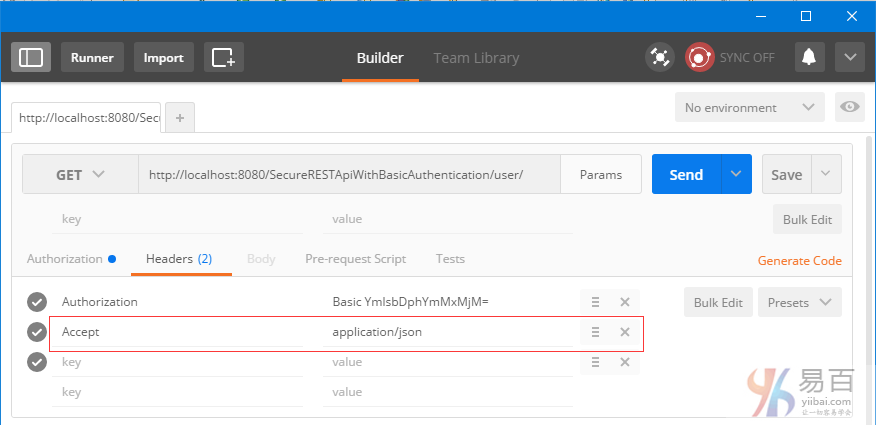
點擊頭(Headers )標籤。您應該看到新的頭。讓我們添加「Accept」頭以及執行JSON響應。如下圖中所示 -
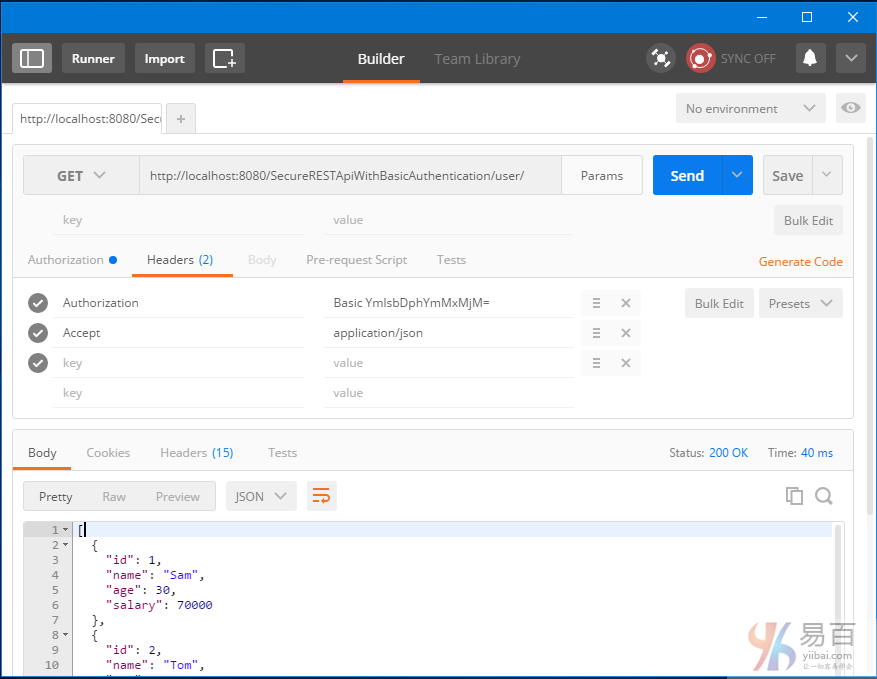
現在發送請求。這個時候您應該看到響應的用戶列表了。
使用客戶端2:基於RestTemplate Java應用程序
讓我們用一個完全成熟的Java客戶端來訪問REST API。我們將使用Spring RestTemplate 發送請求。以瞭解我們如何爲每個請求設置請求頭,發送請求之前要特別注意。
package com.yiibai.springmvc;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.yiibai.springmvc.model.User;
public class SpringRestClient {
public static final String REST\_SERVICE\_URI = "http://localhost:8080/SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication";
/\*
\* Add HTTP Authorization header, using Basic-Authentication to send user-credentials.
\*/
private static HttpHeaders getHeaders(){
String plainCredentials="bill:abc123";
String base64Credentials = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(plainCredentials.getBytes()));
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", "Basic " + base64Credentials);
headers.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION\_JSON));
return headers;
}
/\*
\* Send a GET request to get list of all users.
\*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static void listAllUsers(){
System.out.println("\\nTesting listAllUsers API-----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<List> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/", HttpMethod.GET, request, List.class);
List<LinkedHashMap<String, Object>> usersMap = (List<LinkedHashMap<String, Object>>)response.getBody();
if(usersMap!=null){
for(LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map : usersMap){
System.out.println("User : id="+map.get("id")+", Name="+map.get("name")+", Age="+map.get("age")+", Salary="+map.get("salary"));;
}
}else{
System.out.println("No user exist----------");
}
}
/\*
\* Send a GET request to get a specific user.
\*/
private static void getUser(){
System.out.println("\\nTesting getUser API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/1", HttpMethod.GET, request, User.class);
User user = response.getBody();
System.out.println(user);
}
/\*
\* Send a POST request to create a new user.
\*/
private static void createUser() {
System.out.println("\\nTesting create User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
User user = new User(0,"Sarah",51,134);
HttpEntity<Object> request = new HttpEntity<Object>(user, getHeaders());
URI uri = restTemplate.postForLocation(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/", request, User.class);
System.out.println("Location : "+uri.toASCIIString());
}
/\*
\* Send a PUT request to update an existing user.
\*/
private static void updateUser() {
System.out.println("\\nTesting update User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
User user = new User(1,"Tomy",33, 70000);
HttpEntity<Object> request = new HttpEntity<Object>(user, getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/1", HttpMethod.PUT, request, User.class);
System.out.println(response.getBody());
}
/\*
\* Send a DELETE request to delete a specific user.
\*/
private static void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("\\nTesting delete User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
restTemplate.exchange(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/3", HttpMethod.DELETE, request, User.class);
}
/\*
\* Send a DELETE request to delete all users.
\*/
private static void deleteAllUsers() {
System.out.println("\\nTesting all delete Users API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
restTemplate.exchange(REST\_SERVICE\_URI+"/user/", HttpMethod.DELETE, request, User.class);
}
public static void main(String args\[\]){
listAllUsers();
getUser();
createUser();
listAllUsers();
updateUser();
listAllUsers();
deleteUser();
listAllUsers();
deleteAllUsers();
listAllUsers();
}}
看到上面程序的輸出是:
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=1, Name=Sam, Age=30, Salary=70000.0
User : id=2, Name=Tom, Age=40, Salary=50000.0
User : id=3, Name=Jerome, Age=45, Salary=30000.0
User : id=4, Name=Silvia, Age=50, Salary=40000.0
Testing getUser API----------
User [id=1, name=Sam, age=30, salary=70000.0]
Testing create User API----------
Location : http://localhost:8080/SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication/user/5
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=1, Name=Sam, Age=30, Salary=70000.0
User : id=2, Name=Tom, Age=40, Salary=50000.0
User : id=3, Name=Jerome, Age=45, Salary=30000.0
User : id=4, Name=Silvia, Age=50, Salary=40000.0
User : id=5, Name=Sarah, Age=51, Salary=134.0
Testing update User API----------
User [id=1, name=Tomy, age=33, salary=70000.0]
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=1, Name=Tomy, Age=33, Salary=70000.0
User : id=2, Name=Tom, Age=40, Salary=50000.0
User : id=3, Name=Jerome, Age=45, Salary=30000.0
User : id=4, Name=Silvia, Age=50, Salary=40000.0
User : id=5, Name=Sarah, Age=51, Salary=134.0
Testing delete User API----------
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=1, Name=Tomy, Age=33, Salary=70000.0
User : id=2, Name=Tom, Age=40, Salary=50000.0
User : id=4, Name=Silvia, Age=50, Salary=40000.0
User : id=5, Name=Sarah, Age=51, Salary=134.0
Testing all delete Users API----------
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
No user exist----------
在本實例中所使用的服務如下。完整的代碼可以在本文章的結尾部分下載。
package com.yiibai.springmvc.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.yiibai.springmvc.model.User;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private static final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
private static List<User> users;
static{
users= populateDummyUsers();
}
public List<User> findAllUsers() {
return users;
}
public User findById(long id) {
for(User user : users){
if(user.getId() == id){
return user;
}
}
return null;
}
public User findByName(String name) {
for(User user : users){
if(user.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(name)){
return user;
}
}
return null;
}
public void saveUser(User user) {
user.setId(counter.incrementAndGet());
users.add(user);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
int index = users.indexOf(user);
users.set(index, user);
}
public void deleteUserById(long id) {
for (Iterator<User> iterator = users.iterator(); iterator.hasNext(); ) {
User user = iterator.next();
if (user.getId() == id) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
public boolean isUserExist(User user) {
return findByName(user.getName())!=null;
}
public void deleteAllUsers(){
users.clear();
}
private static List<User> populateDummyUsers(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User(counter.incrementAndGet(),"Sam",30, 70000));
users.add(new User(counter.incrementAndGet(),"Tom",40, 50000));
users.add(new User(counter.incrementAndGet(),"Jerome",45, 30000));
users.add(new User(counter.incrementAndGet(),"Silvia",50, 40000));
return users;
}}
工程目錄結構
最後,下面示出的是本例項目的結構。
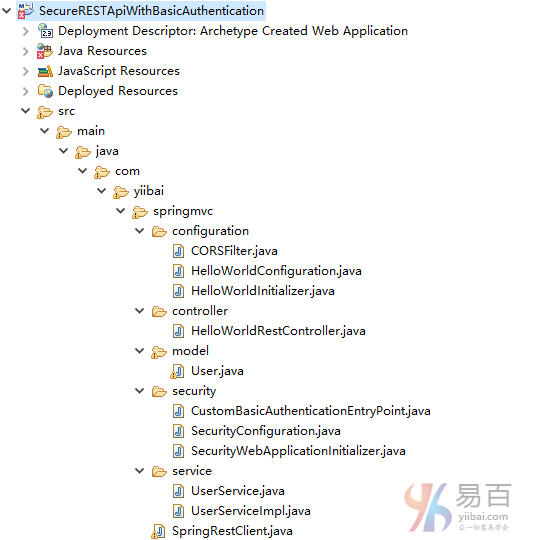

下載源代碼
SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication.zip