Spring Security使用@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize, @Secured方法安全
這篇教程文章中我們來學習 Spring Security使用 @PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize,@Secured和Spring EL表達式的方法級安全。
爲了使使用Spring的方法級別安全,我們需要用註釋一個 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity類在@Configuration,如下圖所示:
package com.yiibai.springsecurity.configuration;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("yiibai").password("123456").roles("USER");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("admin").password("123456").roles("ADMIN");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("dba").password("123456").roles("ADMIN","DBA");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").access("hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') or hasRole('DBA')")
.and().formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.usernameParameter("ssoId").passwordParameter("password")
.and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/Access\_Denied");
}}
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 啓用 Spring Security 全局方法可以使用如下XML配置:
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.0.xsd">
<http auto-config="true" >
<intercept-url pattern="/" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
<intercept-url pattern="/home" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
<form-login login-page="/login"
username-parameter="ssoId"
password-parameter="password"
authentication-failure-url="/Access\_Denied" />
</http>
<global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"/>
<authentication-manager >
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="bill" password="abc123" authorities="ROLE\_USER" />
<user name="admin" password="root123" authorities="ROLE\_ADMIN" />
<user name="dba" password="root123" authorities="ROLE\_ADMIN,ROLE\_DBA" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>需要注意的是@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity需要幾個參數,如下所示:
- prePostEnabled :確定 Spring Security 前置註釋 [@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize,..] 是否應該啓用;
- secureEnabled : 確定 Spring Security 安全註釋 [@Secured] 是否應該啓用;
- jsr250Enabled : 確定 JSR-250註釋 [@RolesAllowed..] 是否應該啓用;
可以在同一應用程序啓動一個以上的類型的註釋,但只有一種類型用於接口或類的行爲(在類的行爲沒有明確定義時)。如果找到兩個註解適用於特定的方法,那麼只有其中的一個被應用。
我們將探討上面兩個提到細節。
@Secured
@Secured註釋是用來定義業務方法的安全性配置屬性列表。您可以使用@Secured在方法上指定安全性要求[角色/權限等],只有對應角色/權限的用戶纔可以調用這些方法。如果有人試圖調用一個方法,但是不擁有所需的角色/權限,那會將會拒絕訪問將引發異常。
@Secured是從之前Spring版本中引入進來的。它有一個缺點(限制)就是不支持Spring EL表達式。考慮下面的例子:
package com.yiibai.springsecurity.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
public interface UserService {
List<User> findAllUsers();
@Secured("ROLE\_ADMIN")
void updateUser(User user);
@Secured({ "ROLE\_DBA", "ROLE\_ADMIN" })
void deleteUser();}
在上面的例子中,UpdateUser方法可以由具有 Admin 角色的人調用,而deleteUser可以由DBA或管理員角色的人被調用。如果不擁有所需的角色而試圖調用一個方法,那麼將一個訪問拒絕並將引發異常。
如果你想要指定「AND」條件。想調用deleteUser方法同時擁有ADMIN和DBA角色的用戶。這是不可能繞過 @Secured 註釋的。
這可以使用 Spring 新的 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 註解來支持 Spring EL 。
@PreAuthorize / @PostAuthorize
Spring 的 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 註解是首選應用到方法級安全性的方式,並支持Spring表達式語言,也提供基於表達式的訪問控制。
@PreAuthorize適合進入方法之前驗證授權。 @PreAuthorize可以兼顧,角色/登錄用戶權限,參數傳遞給方法等等。
@PostAuthorize 雖然不經常使用,檢查授權方法之後才被執行,所以它適合用在對返回的值作驗證授權。Spring EL提供可在表達式語言來訪問並從方法返回 returnObject 對象來反映實際的對象。
請參見常見 內置表達式瞭解支持表達式的完整列表。讓我們回到之前的例子,這一次使用 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 。
package com.yiibai.springsecurity.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import com.yiibai.springsecurity.model.User;
public interface UserService {
List<User> findAllUsers();
@PostAuthorize ("returnObject.type == authentication.name")
User findById(int id);
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
void updateUser(User user);
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') AND hasRole('DBA')")
void deleteUser(int id);}
由於@PreAuthorize可以使用Spring表達式語言,任何條件可以很容易地使用EL來表示。deleteUser 方法現在配置以通過同時擁有ADMIN和DBA角色的用戶調用。
此外,我們還在 findById()方法上添加了註解 @PostAuthorize 。使用@PostAuthorize,從方法(用戶對象)返回的值將是使用 returnObject 對象訪問在Spring表達式語言中,並且返回用戶對象的個別屬性可以應用到一些安全規則。在這個例子中,我們要確保登錄的用戶只能得到它自己的用戶類型對象。
這是所有關於@Secured,@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize和EL的基本用法。
以下在這個例子中要使用的服務實現,用戶模型類和控制器等。代碼如下所示 -
package com.yiibai.springsecurity.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.yiibai.springsecurity.model.User;
@Service("userService")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
static List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
static{
users = populateUser();
}
public List<User> findAllUsers(){
return users;
}
public User findById(int id){
for(User u : users){
if(u.getId()==id){
return u;
}
}
return null;
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
System.out.println("Only an Admin can Update a User");
User u = findById(user.getId());
users.remove(u);
u.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
u.setLastName(user.getLastName());
u.setType(user.getType());
users.add(u);
}
public void deleteUser(int id){
User u = findById(id);
users.remove(u);
}
private static List<User> populateUser(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User(1,"Sam","Disilva","admin"));
users.add(new User(2,"Kevin","Brayn","admin"));
users.add(new User(3,"Nina","Conor","dba"));
users.add(new User(4,"Tito","Menz","dba"));
return users;
}}
public class User {
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String type;//getters/setters
}
package com.yiibai.springsecurity.controller;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.SecurityContextLogoutHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.yiibai.springsecurity.model.User;
import com.yiibai.springsecurity.service.UserService;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@Autowired
UserService service;
@RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listAllUsers(ModelMap model) {
List<User> users = service.findAllUsers();
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "allusers";
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String editUser(@PathVariable int id, ModelMap model) {
User user = service.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("edit", true);
return "registration";
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String updateUser(User user, ModelMap model, @PathVariable int id) {
service.updateUser(user);
model.addAttribute("success", "User " + user.getFirstName() + " updated successfully");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/delete-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable int id) {
service.deleteUser(id);
return "redirect:/list";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/Access\_Denied", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String accessDeniedPage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
return "accessDenied";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String loginPage() {
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String logoutPage (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (auth != null){
new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, auth);
}
return "redirect:/login?logout";
}
private String getPrincipal(){
String userName = null;
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
userName = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
} else {
userName = principal.toString();
}
return userName;
}}
這個例子完整的代碼附加在這篇文章的末尾。有需要練習或參考可自行下載(不收費)。
部署和運行
下載並安裝在帖子的末尾完整的示例代碼。部署它到Servlet3.0容器(例如:Tomcat 8.0.21)。
打開瀏覽器,並打開網址:http://localhost:8080/SpringSecurityMethodLevelSecurityAnnotation/, 系統將提示您登錄。
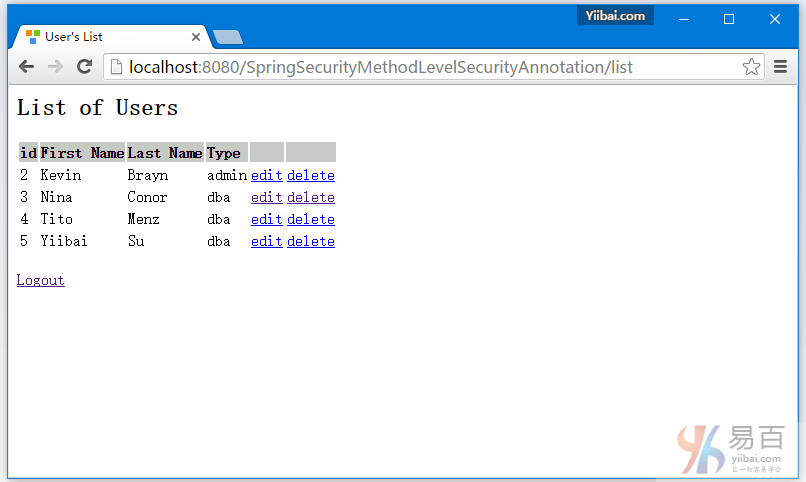
提交後,您會看到一個用戶列表。
現在嘗試編輯或刪除用戶,你應該看到拒絕訪問頁面,因爲此用戶角色無權訪問這些功能。
現在註銷登錄。重新使用 admin 角色的用戶(admin / 123456)登錄。
提交後,你會看到用戶列表,如下圖中所示 -
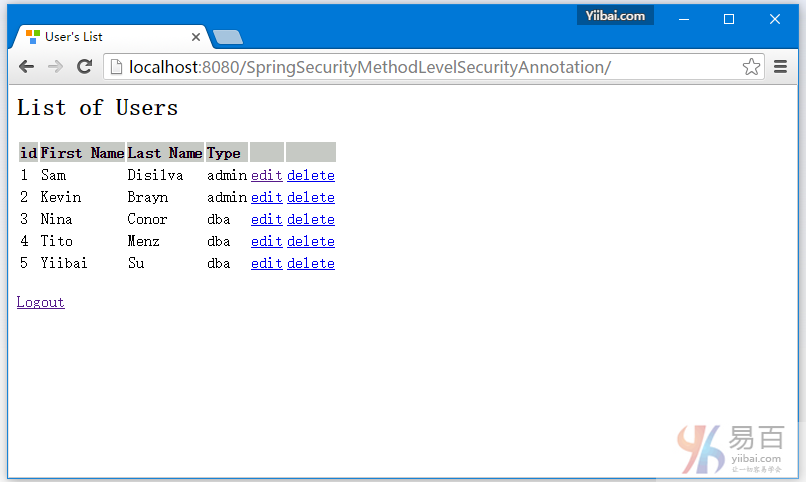
現在點擊編輯第一行[type='admin']。編輯頁面應該出現。
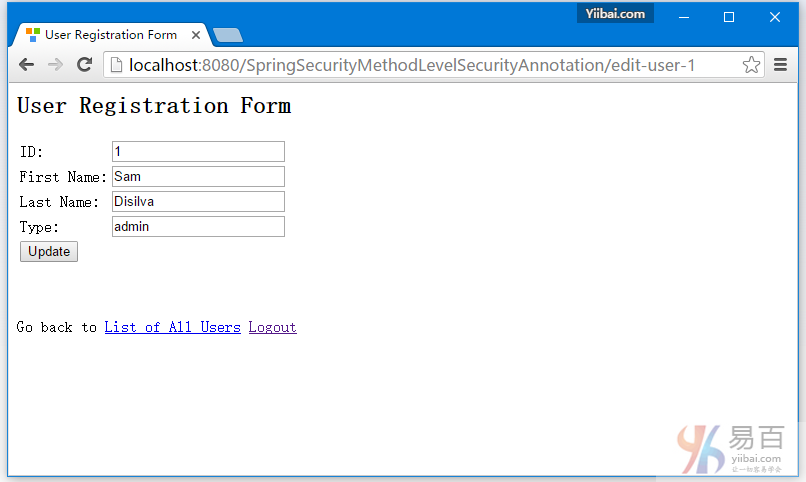
現在回到記錄列表中,點擊第三行[type = 'dba'],如下所示 -
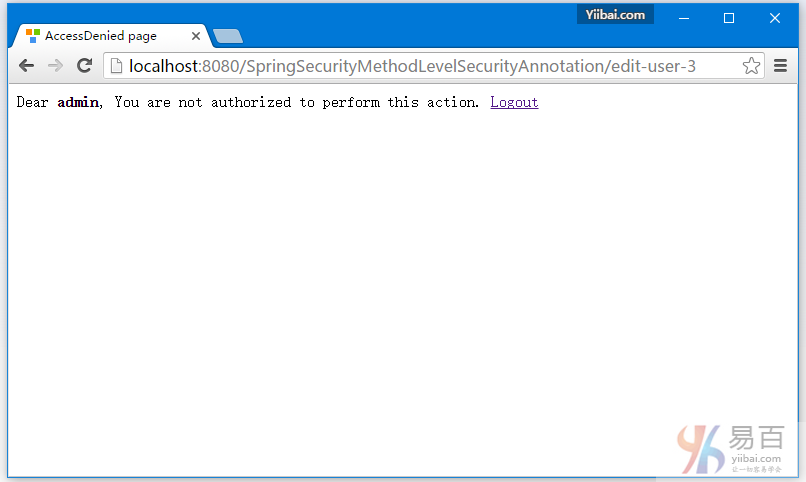
在執行編輯時訪問拒絕,findById()函數調用了使用EL限制的 @PostAuthorize註釋,返回的對象只能與類型爲['dba']一樣的登錄用戶名才能操作。
現在點擊任何刪除行應該會顯示拒絕訪問,因爲只允許角色爲「DBA」的用戶才能刪除用戶。
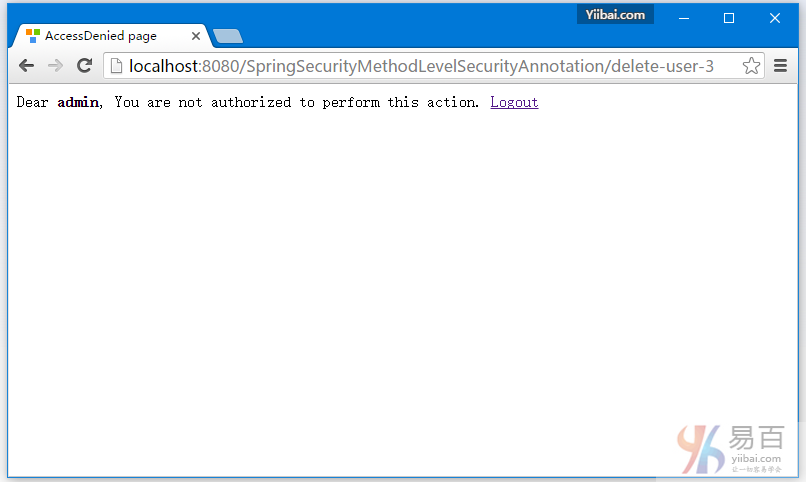
現在註銷,登錄一個具有DBA角色的用戶[dba,123456],然後點擊第一行的刪除鏈接,這一行記錄應該會被成功刪除。其它更多的操作您可以試着去摸索。
就這麼多,包教不包會。
下載源代碼
12-SpringSecurityMethodLevelSecurityAnnotation.zip