Java設計模式
Java工廠設計模式
Java抽象工廠模式
Java單例模式
Java建造者(Builder)模式
Java原型模式
Java適配器模式
Java橋接模式
Java過濾器模式(條件模式)
Java組合模式
Java裝飾模式
Java門面模式(或外觀模式)
Java享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)
Java責任鏈模式
Java命令模式
Java迭代器模式
Java中介者模式(Mediator Pattern)
Java解釋器模式
Java備忘錄模式
Java觀察者模式
Java狀態模式
Java空對象模式
Java策略模式
Java模板模式
Java訪問者模式
Java MVC模式
Java業務代理模式
Java組合實體模式
Java數據訪問對象模式
Java前端控制器模式
Java攔截過濾器模式
Java服務定位器模式
Java傳輸對象模式
Java享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)主要用於減少創建的對象數量,並減少內存佔用並提高性能。 這種類型的設計模式屬於結構模式,因爲該模式提供了減少對象計數的方法,從而改善應用的對象結構。
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)嘗試通過存儲已經存在的類似對象以重用,並在找不到匹配的對象時創建新對象。我們將通過繪製不同位置的20個圓圈來演示這種模式,但是這裏只創建5個對象。只有5種顏色可用,因此color屬性用於檢查已經存在的Circle對象。
實現實例
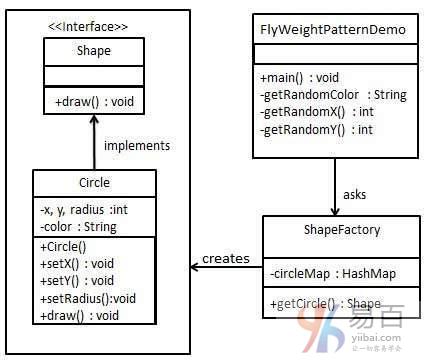
在這個實例中,將創建一個Shape接口和一個實現Shape接口的具體類Circle。在下一步中將定義一個工廠類ShapeFactory。
ShapeFactory有一個HashMap的Circle作爲Circle對象的顏色。每當一個請求向ShapeFactory創建一個指定顏色的圓形時,它會檢查HashMap中的圓形對象,如果找到對象則返回這個對象,否則就會創建一個新對象然後存儲在hashmap中以供將來使用,並返回這個新創建的對象給客戶端。
FlyWeightPatternDemo這是一個演示類,將使用ShapeFactory來獲取一個Shape對象。它將信息(紅色/綠色/藍色/黑色/白色)傳遞給ShapeFactory以獲得所需顏色的圓形。
享元模式的實現實例結構如下圖中所示 -
第1步
創建一個接口,如下代碼 -
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}第2步
創建一個實現相同接口的具體類。
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color + ", x : " + x + ", y :" + y + ", radius :" + radius);
}
}第3步
創建一個工廠根據給定的信息生成具體類的對象。
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
private static final HashMap<String, Shape> circleMap = new HashMap();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}第4步
使用工廠並通過傳遞諸如顏色的信息來獲得具體類的對象。
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] = { "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle = (Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}第5步
驗證輸出,執行上面的代碼得到以下結果 -
Creating circle of color : Black
Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Green
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100
Creating circle of color : White
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Red
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Blue
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100